Imaging Experts
OUR SERVICES
At Pueblo Radiology, we provide the newest and most advanced imaging services. Find specifics about each imaging modality, including what to expect, and frequently asked questions.
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
What Is Magnetic
Resonance Imaging?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a sophisticated medical imaging technique that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the inside of the body. Unlike X-ray exams or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe and noninvasive option for medical diagnosis. MRI is particularly useful for visualizing soft tissues and frequently used when evaluating organs, muscles, joints, breast tissue, the spine, and the brain. Its versatility and ability to produce detailed images make MRI an essential tool in modern medicine for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
LOOKING FOR WHOLE BODY MRI?click for more info +
what to expect:
BEFORE
Prior to your exam, you may continue your normal dietary regime. Upon your arrival, we will ask you to change into a cotton gown and remove all metal objects if you have not already done so. Some of these objects include jewelry, metal zippers or buttons, hairpins and hearing aids. Please notify our office ahead of time if you have any metal devices inside your body or if you are pregnant.
DURING
For the duration of your exam you will be asked to lie still on a table so that the MRI can produce the highest quality images. During scanning, there will be a loud (at times very loud) knocking noise; during imaging, we will provide you with earplugs and/or headphones with music to minimize this noise. You will also be able to communicate through an intercom with our technologists if you are feeling any discomfort. The entire exam usually lasts around 20 to 30 minutes; some exams can last up to one hour.
AFTER
After your exam, you can return to your normal routine. Our highly trained radiologists will analyze your images and report the findings to your doctor.
OUR TECHNOLOGY
PHILIPS MR5300 1.5T
In the first quarter of 2024, Pueblo Radiology invested in a new MRI technology from Philips Medical designed for those patients with claustrophobia or MRI-based anxiety. The Ambient Experience unique to this scanner, provides the patient with an immersive viewing experience for scans involving the head, neck, upper extremities, chest, and abdomen. Soothing communication and music will be heard through headphones, keeping the patient informed as they move through their scan. As with our other MRI scanners, this new scanner also has a large opening with a short bore design, meaning that for most of the lower extremity exams, the patient’s head will be out of the scanner. Lastly, the scanner’s advanced technology will provide faster scan times, meaning less time in the scanner for the patient. As compared to “open” MRI scanners, our scanner is faster with significantly better image quality.
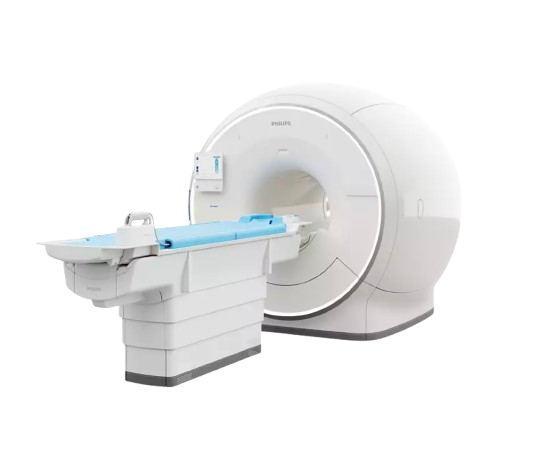
siemens verio 3t
Our Verio MRI is a high field strength unit with a large opening, 27 1/2” diameter, the same as our 1.5T MRI scanners. This MRI, accommodates patients of up to 550lbs and with the field strength of the magnet, Pueblo is able to acquire outstanding images with relatively short exam times.
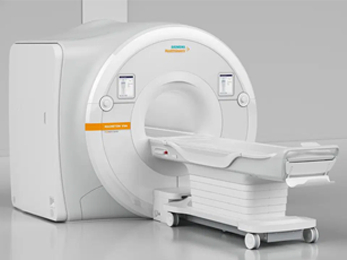
SIEMENS ALTEA 1.5T
In September of 2021, Pueblo Radiology upgraded to a new MRI platform called Magnetom Altea. This 1.5T MRI scanner has features that support state-of-art imaging as well as maximize patient comfort. The user-friendly operating system, combined with a sophisticated scanning capability, allows us to reduce the time patients spend in on the scanner. The magnet itself has a patient-friendly space with a wide aperture and short bore length, combined with soothing lighting and air conditioning within the scanner. Patients having scans on older scanners have been impressed with the shortened exam times and high level of comfort provided by this new system.
FAQs
All Pueblo MRI units are wide bore meaning the opening is larger than compared to older style systems. Additionally all of our MRI units are sort front-to-back so patients feel less like being in a “tunnel”. All our units are high field systems generating extraordinary images. MRI is safe. You will be given a safety questionnaire prior to your scan. Patients with metal surgical implants or electronic devices may require special measures to get their scan accomplished.
MRI does not use x-ray like other imaging techniqures (e.g. CT). Instead MRI uses a combination of magnets and rediofrequency energy to generate the images.
Our magnets have among the largest openings and shortest lengths in the MRI market. Additionally, through the use of artificial intelligence (AI), our scan times can be significantly shorter than what you may have experienced in the past. One of our scanners has a visual panoramic movie display that patients can see with the use of a headset. This allows patients to feel more comfortable and less confined.
You will not be able to wear clothing that has any metal on it or clothing that is made with any form of metallic thread (e.g. some yoga & athletic wear). We will provide a cotton top and pants as necessary for your exam. Ideally, we would prefer that you remove and leave all jewelry at home.
We prefer that only the patient be in the scan room. Special consideration will be considered for minors and special needs patients.
Gadolinium is a contrast material used in some MRI exams. Gadolinium is injected intravenously through an IV set up in your arm. The gadolinium used in MRI is very safe though some patients have had sensitivity similar to an allergic reaction. Please let our staff know if you have had any prior issues related to MRI or gadolinium.
Plan to spend 30-60 minutes for your MRI appointment. Your actual time on the magnet will vary.
Throughout the examination your technologist will be able to see and hear you during your scan. An intercom system and a “squeeze” ball will be in place so you can communicate with the technologist if necessary. To avoid motion during the scan, you will need to lie still and silent on the table. At various times during your scan, our technologist will check in with you via the intercom.
Whole Body MRI
CT
Computed Tomography
What Is Computed Tomography?
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are a quick and painless way to examine any part of the body when there is a clinical reason to suspect internal injury, disease, tumor or infection. To do this, a series of x-rays are taken from different angles around the body, combined and then processed by a powerful computer to create cross-sectional images of your body. Another way to think of the images are like slices of a loaf of bread.
what to expect:
BEFORE
Preparation for CT scans depends on which area of your body is being examined. Upon arrival, you may be asked to wear a gown. Sometimes you will be asked to drink water prior to your examination. Please call our office at 805.682.7744 with any questions.
DURING
For the duration of your CT scan, you will be asked to lie very still on a table connected to the scanner. As the table moves through the large opening, your technologist may assist you and communicate further instructions. Each scan takes about 20 to 40 seconds and the entire exam may last for 20 minutes. For many exams, an IV will be started to allow the injection of contrast material (radiology dye). This improves identification of blood vessels and various organs.
AFTER
Following your CT appointment, you can return to your normal daily activities. Our radiologist will interpret your CT exam and issue a report with the exam findings to your physician(s).
OUR TECHNOLOGY
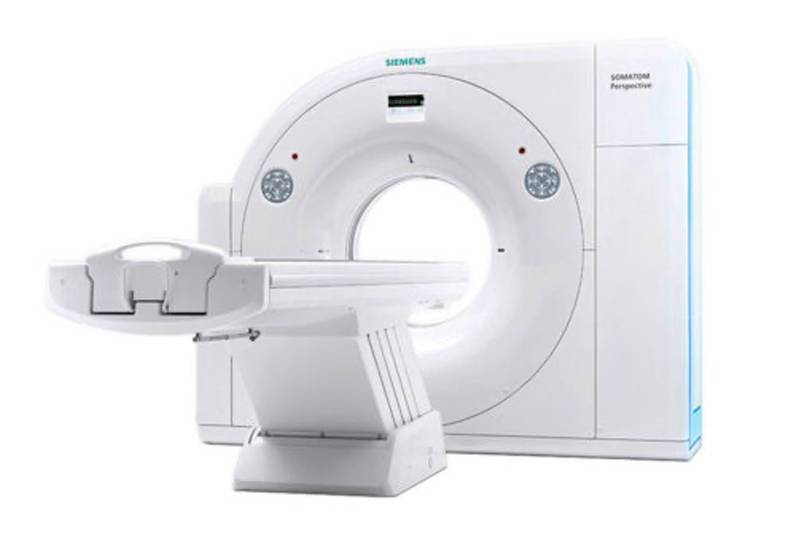
Siemens 64-Slice Perspective CT Scanner
Pueblo Radiology operates a 64-Slice Perspective CT Scanner. One of the key features of this machine is the advanced dose reduction. Doses are automated according to each patients’ anatomy resulting in a 60% dose reduction across the board. In addition, this machine offers high-quality vascular imaging and a faster scanning speed enabling visualization of even the smallest diagnostic detail. Lastly, the patient friendly design allows easier access and positioning for patients, giving them more time with the technologists.
FAQs
Contrast allergy; in certain CT examinations requiring visualization of the body’s vascular structures, an iodine-based contrast agent, is injected intravenously during scanning. Commonly the injection site is the elbow area of the arm (like a blood draw for lab work). When you arrive you will answer a questionnaire to see if you have any allergies that might make you more likely to have an allergic reaction to the iodinated contrast. If you know you are allergic to iodine, or “x-ray dye”, please inform our staff at the time of scheduling so we can make the necessary pre-procedure arrangements. This material is not radioactive.
Radiation dose; Pueblo has a CT scanner that was developed to utilize the minimum dose necessary in providing high quality diagnostic images. We operate our CT scanner with techniques that allow us to use the lowest possible radiation dose while maintaining improved image quality. While radiation dose has been a concern in the past and we continue to need to use it appropriately, you can be assured that the radiation dose associated with your scan will be kept as low as possible.
After a barium swallow or upper GI exam, the barium moves through your digestive system and is mostly excreted in your stool. It may take 1-2 days to fully pass. Barium can cause constipation and make stools appear white. Drinking fluids and eating fiber can help prevent constipation. If you experience severe pain or difficulty passing stool, contact your doctor.
While you can request medication from your physician to relieve the claustrophobia, it has been our experience that very few people are claustrophobic in our CT scanner. The scanner opening is 70cm (27.6″) across and the depth of the scanner in the opening is only 27″. If you would like to visit our office to see what our scanner looks like prior to your appointment, we are happy to arrange that in hopes that your visit will then go more smoothly and with lower anxiety.
Yes, CT scans do produce more radiation than a regular x-ray. The result of a regular X-ray is a 2D image while a CT scan will provide your doctor with a 3D image. You will get significantly more information out of a CT scan than an x-ray. In addition to providing use with the highest quality images the scanner has automated low-dose technology which decreases the amount of radiation by over one-third of what was previously used.
Oral contrast is used in a CT scan to enhance visibility of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, helping to highlight structures like the stomach and intestines. It makes it easier to detect issues such as inflammation, blockages, or tumors. The contrast improves image clarity and allows better differentiation of organs. It’s commonly required for abdominal or pelvic scans to assess both the digestive system and surrounding organs. Pueblo uses water as an oral contrast and in some instances water mixed with iodine.
IV contrast in CT is an iodine-based contrast agent injected into a vein to improve image quality. It enhances the visibility of blood vessels, organs, and tissues, helping to detect issues like blockages, tumors, or bleeding. It provides clearer, more detailed images of the body, aiding in diagnosis.
ULTRASOUND
What Is ULTRASOUND?
Diagnostic Ultrasound is an imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of certain structures within your body. Ultrasounds are painless and used for a variety of reasons including diagnosing some forms of cancer or infection and evaluating abnormalities within your body. Our specially-trained technologists use a device called a transducer during this exam, which, when placed on your skin, emits pulses of sound waves that parts of your body reflect back. All of this information is then sent to a computer which composes detailed images based on patterns created by these sound waves.
what to expect:
BEFORE
Preparation depends on the area of your body which is being examined. Some exams mandate withholding food and drink for 4 to 8 hours prior while others require a full bladder. We will provide you with specific instructions to prepare you for your exam at the time of scheduling your appointment.
DURING
For the duration of your Ultrasound, you will be asked to lie on a padded table wearing a gown we will provide for you. Your technologist will then proceed by applying a thin layer of gel to the area being scanned, and gently press and slide the transducer on your skin. The entire procedure varies from 15 to 60 minutes depending on which area of your body is being examined.
AFTER
After your exam, you can return to your activities as normal. Our highly trained radiologists will analyze your images and report the findings to your doctor who will then followup with you with regard to the results.
FAQs
There are no risks associated with ultrasound imaging.
None. Ultrasound uses sound wave energy to create the images.
Wear comfortable clothing, but you may need to change into a gown that we provide. No need to remove jewelry.
Only under pre-arranged conditions.
Most ultrasound exams take 15-45 minutes.
You will lie on a gurney in a position that allows our technologist the ability to scan the area of interest. Most times this is with you lying on your back in a supine position.
X-RAY
What are x-rays?
Since their discovery in 1895 by the German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen, X-rays have played a major role in helping physicians diagnose and treat disease. X-rays are high-energy electro-magnetic waves created within an x-ray tube. They are highly penetrating, and in combination with computers and special imaging plates, provide images of various internal organs and structures.
Your physician and the radiologist combine to provide you with the test best suited to your particular situation. While all radiation exposure carries some risk, the benefits of diagnosing your condition far outweigh these risks. Today’s x-ray exams are performed with very low radiation exposure.
X-ray examinations are carried out by licensed technologists and interpreted by physicians (radiologists) who are specially trained in the imaging sciences.
While most x-ray exams are related to skeletal structures (bones) and surrounding soft tissues, there are some x-rays that require the use of contrast material so that the areas of interest show up on the images.
Common X-Ray Procedures:
Upper GI
An Upper Gastrointestinal Series (UGI) is a diagnostic medical test used to examine the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). This test involves drinking a barium solution and taking X-ray images to detect abnormalities like ulcers, tumors, or blockages.
FAQs
No, most patients tolerate the flavor of the barium well.
Drinking barium is required for barium swallow and upper GI exams to help highlight your digestive system on the images. Barium is a contrast material that absorbs X-rays, making the stomach, intestines, and other GI structures more visible. This allows doctors to better detect issues such as blockages, inflammation, tumors, or abnormalities in the digestive tract. In short, drinking barium improves the clarity of images of your GI system, making it easier for your doctor to assess any potential problems.
After a barium enema exam, the barium moves through your digestive system and is mostly excreted in your stoool. It may take 1-2 days to fully pass. Barium can cause constipation and make stools appear white. Drinking fluids and eating fiber can help prevent constipation. If you experience severe pain or difficulty passing stool, contact your doctor.
Lower GI / Barium Enema
A Lower GI, also known as a barium enema, is a diagnostic test used to examine the lower gastrointestinal tract. The barium is administered through a tube and inserted in the rectum. The radiologist will then watch your colon fill with this combination of barium and air, positioning you as needed so that the barium fills your colon. The radiologist will take a series of images during this process. Once the imaging is complete, the barium will drain back into a bag, and you will be escorted to the restroom to further remove any remaining barium. This combination of barium is used in diagnosing conditions such as polyps, tumors, diverticulosis, and inflammatory conditions (colitis).
FAQs
The barium (and maybe air) allow the radiologist to see structures that would otherwise not be well seen on regular x-ray images.
After a barium enema exam, the barium moves through your digestive system and is mostly excreted in your stoool. It may take 1-2 days to fully pass. Barium can cause constipation and make stools appear white. Drinking fluids and eating fiber can help prevent constipation. If you experience severe pain or difficulty passing stool, contact your doctor.
No, you can return to normal activities. Actively moving/exercising will encourage any remaining barium to pass out of your colon.
Hysterosalpingography
A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) is a diagnostic X-ray procedure used to evaluate the uterus and fallopian tubes (oviduct), often performed to investigate infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
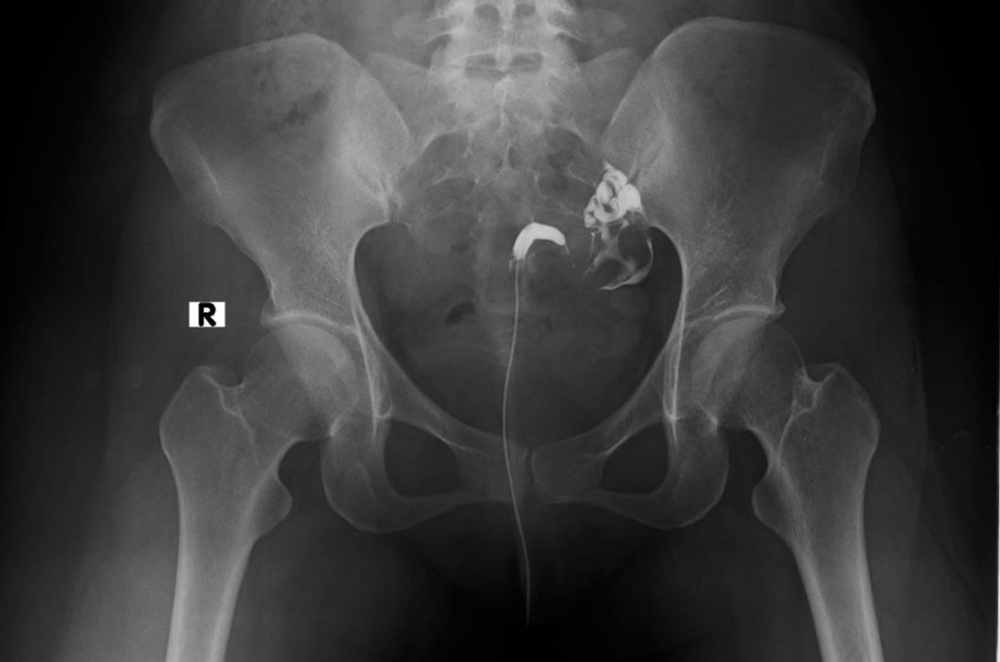
FAQs
A catheter will be placed through the cervix by a Pueblo radiologist. An iodine-based contrast material (“x-ray dye”) will be injected into the uterus while the radiologist watches the uterus and oviducts fill under x-ray guidance. In cases of infertility, the radiologist will be looking for the contrast material to “spill” into the abdominal cavity, indicating that the oviducts re unobstructed.
The contrast material is sterile when injected, and that which spills is naturally absorbed in the abdomen and excreted in the urine. The patient will see no change in urine color or consistency.
When the exam is completed, the catheter is removed and the patient is dismissed. Since residual contrast may continue to seep down from the uterus and you may have some spotting. It is recommended that you wear a pad for a few hours following the test. Normally, no sedation is given for a hysterosalpingogram so you can drive home.
Most women will experience some cramping during the examination. The severity varies person to person but only lasts for a minute or two and will resolve completely following the procedure.
It will not influence your ability to become pregnant. In fact, it is not uncommon for a woman who was previously having trouble becoming pregnant to get pregnant following the test.
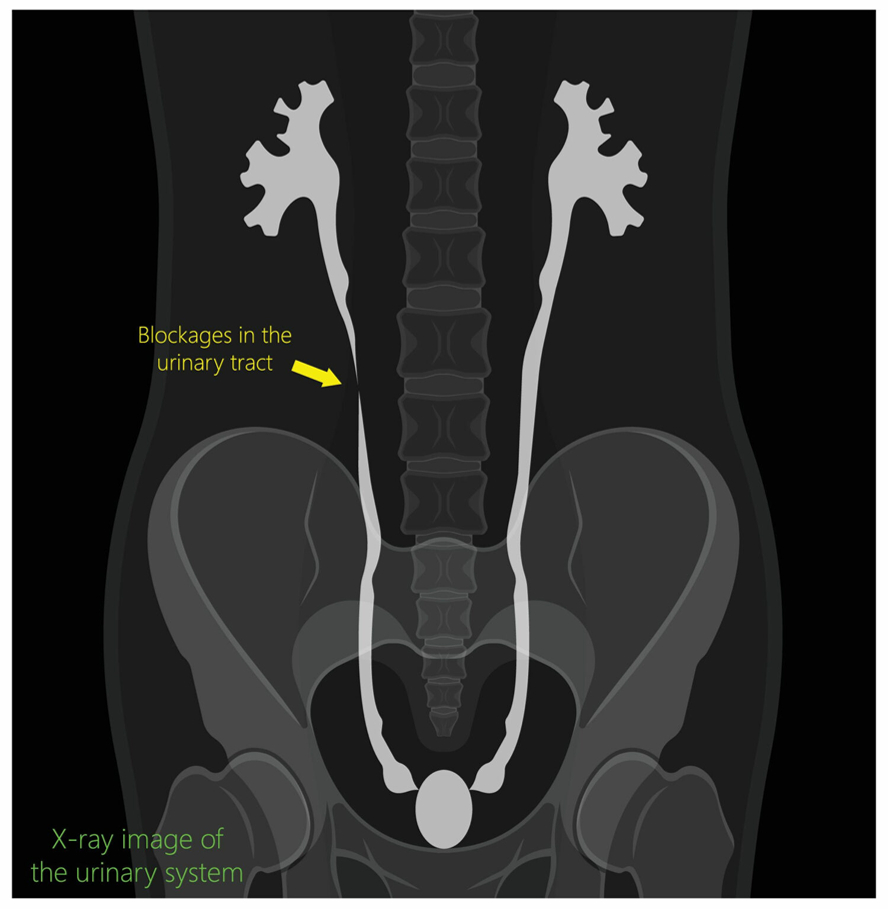
Cystogram / VCUG
These x-ray procedures are done in evaluating problems associated with the urinary tract. In some cases, they are done following surgery to assure that the urinary tract is healing and functioning properly.
A cystogram is a test where contrast material (dye) is injected into your bladder through a catheter (soft flexible tubing) placed in your urethra. If the urethral catheter is not in place we will put it in prior to the test. The contrast material will fill your bladder and the radiologist will take pictures of the process. Once the imaging is complete, the contrast will be drained out of your bladder.
A voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) is an X-ray procedure to evaluate the bladder and urethra. A catheter is inserted into the urethra and contrast material is injected by the radiologist. X-rays are taken as the radiologist watches the bladder fill. Following the bladder filling, the catheter is removed and the patient is encouraged to urinate while the radiologist watches and records images of the process.
FAQs
It is excreted normally in your urine. As the contrast is mostly clear, you will notice no color change in your urine.
Mammography
at santa barbara women’s imaging center
DEXA
BONE DENSITY TESTING
What is bone density testing (dexa)?
Osteoporosis is a disease which makes bones fragile and weak, and therefore more prone to fracture. Osteoporosis affects 54 million Americans, mostly women. Studies show that one in two women and one in four men age 50 and older will break a bone due to Osteoporosis. The condition is treatable and may be preventable. People need to know their risk for osteoporosis and talk to their doctors about diagnosis, prevention and treatment.
Osteoporosis Risk Factors
- Age
- Gender
- Family history
- Race
- Bodyweight
- Menopause
- Lifestyle
- Medications
BEFORE THE EXAM:
PREPARATION FOR THE EXAM
- While there is no special preparation. You may eat normally but do not take any antacids (e.g. Tums / Rolaids) 24-hours prior to your appointment.
- There is no need to disrobe if you wear clothes without buttons, zippers or other metals (underwire included). Loose fitting clothes without metal or plastic such as workout outfits, sweatpants, sweatshirts and sports bras are recommended.
- Do not schedule this exam for at least one week following any kind of barium x-ray study.
- You will be asked to fill out a questionnaire prior to your scan to help our radiologist in interpreting your bone density test.
WHAT TO EXPECT
The test will take approximately 15 minutes. You will be lying on your back throughout your exam. The actual DEXA scan only takes a few minutes. The exam is painless with no injections. Your exam will be reviewed by our radiologist and results will be sent to your physician.
Screening / Preventative
our screening services:
Pueblo Radiology offers an array of screenings tests using mammography, ultrasound, CT scanning and MRI. Our screening exams are performed so that we can detect the presence of many common forms of cancer and disease in their early stages, so that a patient and their physician can take the necessary actions for early intervention. As opposed to the “street corner” parking lot mobile operations that provide a similar service, we only work with a physician referral. We believe that screening imaging studies should be part of a physician-guided comprehensive well-person evaluation; therefore, we strongly urge you to seek the guidance of your physician. In this way, your testing can be tailored to your specific concern, and other important testing, like lab tests, can also be performed.
CT Cardiac Calcium Scoring
CT Cardiac Scoring (also known as a Coronary Calcium Score or Cardiac Calcium Scoring) is a non-invasive medical imaging test used to evaluate the amount of calcium deposits in the coronary arteries. These calcium deposits are an indicator of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, potentially leading to heart disease.
FAQs
You belong to a high-risk group if any of the following factors apply to you:
- You have high cholesterol levels
- You have high triglyceride values
- You smoke
- You have high blood pressure
- You are hereditarily at risk
- You have diabetes
Or any of the factors in combination with a sedentary lifestyle. If one or more of the above points apply to you, contact your physician to find out more about how CT can help in the evaluation of your heart.
This CT exam detects and quantifies calcium deposits in the vessels of the heart. This exam can help predict the likelihood of developing heart disease or having a heart attack before symptoms occur. For those people having one or more risk factors for heart disease, CT cardiac scoring is recommended.
A non-invasive computed tomography (CT) scan captures detailed images of the heart. These images are analyzed by a computer and the amount of calcium detected in the vessels is assigned a score corresponding to level of risk for coronary artery disease: very low – low – moderate – high. Knowing your level of risk will allow you and your doctor to take proactive steps toward managing your cardiovascular health.
CT Lung Screening (low dose)
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends annual screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) in adults aged 50 to 80 years who have a 20 pack-year smoking history. Screening should be discontinued once a person has not smoked for 15 years or develops a health problem that substantially limits life expectancy or the ability / willingness to have curative lung surgery.
FAQs
You belong to a high-risk group if any of the following factors apply to you:
- You smoke
- You are exposed to second-hand smoke
- You are hereditarily at risk for lung cancer
- Asbestos exposure
Or any of the factors in combination with a sedentary lifestyle.
A CT scan is performed, with a low radiation dose, in just 15 seconds. If the result is negative, clinically significant lung lesions/nodules can be excluded with very high probability. If positive, further diagnostic measures appropriate for the severity of the suspected disorder may be are required.
This is a screening technique that has been discussed in recent medical literature as an extremely sensitive method of detecting early and potentially curable lung cancers, while they are still very small nodules, i.e. less than 1 cm in size.
Once the patient is on the CT Scanner, the test should take no more than 15 minutes.
This is not a painful test. There are no injections. It merely requires one to hold their breath for roughly 15-20 seconds.
A negative is never absolute, however, it is extremely accurate in the detection of small lung nodules, the earliest sign of lung cancer. A small cancer that may arise in the tracheobronchial tree may not be detected by this technique. If the test is positive, it means you have one or more small lung nodules. But this does not mean you have lung cancer. The test is designed to detect small nodules in the lung. If you have a positive test (one or more nodules), a high resolution (more detailed) CT Scan will be performed. The purpose of this is to further characterize the lesion, to look for certain features that make it more suspicious for cancer, or more likely to be benign. In addition, depending on the number, size and characteristics of the nodules, some patients will go on to have a lung biopsy. This is usually under CT guidance with local anesthesia. A sample of the nodule is obtained through a needle. Some patients may go directly to surgery. There is a large sub-group of patients who will have a recommendation for a followup study to try to determine the growth of the nodule.
Screening Vascular Ultrasounds
Vascular disease is among the leading causes of death in the United States, yet is generally asymptomatic until a catastrophic event occurs, such as a heart attack, stroke or aneurysm rupture. Pueblo Radiology offers preventive vascular screening ultrasound to bring legitimacy and medical integrity to the “parking lot” screening exams commonly seen in many communities.
Pueblo Radiology’s vascular screening covers three important areas:
- Carotid arteries (neck) – to access stroke risk (more info+)
- Aorta (abdomen) – to detect the presence of aortic aneurysm (more info+)
- Blood pressure assessment of the lower extremities to identify peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and risk of heart disease (more info+)
Together, this three-part assessment can be an important element in determining risk of vascular disease in general, implying relative risk in areas that are more difficult to image, such as the heart (coronary arteries).
Individuals 55 years of age or older with any of the following cardiovascular risk factors may benefit from preventive screening for vascular disease:
- Diabetes mellitus
- History of hypertension
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Known cardiovascular disease
- Smoking
Noninvasive screening examinations have proven to be accurate in detecting vascular disease prior to active warning signs and before a major medical incident such as stroke or sudden death from aneurysm rupture.
FAQs
You belong to a high-risk group if any of the following factors apply to you:
- You have high cholesterol levels
- You have high triglyceride values
- You smoke
- You have high blood pressure
- You are hereditarily at risk
- You have diabetes
Or any of the factors in combination with a sedentary lifestyle. If one or more of the above points apply to you, contact your physician to find out more about how CT can help in the evaluation of your heart.
More information
The abdominal aorta is the main artery of the body. Vascular disease and potentially lethal aneurysms (abdominal aortic aneurysm = AAA) can occur without visible signs or symptoms. Overall, the probability of AAA in the general population is low, but this increases when certain risk factors are present.
These include:
- Age
- Male gender
- White race
- Smoking
- Family History of aneurysms
- History of other vascular aneurysms
- Hypertension
- Atherosclerotic diseases
- Cerebrovascular disease
- High cholesterol
One-time ultrasound screening for AAA is recommended for all men at or older than 65 years. Other appropriate screening conditions include:
- Screening men as early as 55 years is appropriate for those with a family history of AAA
- One-time ultrasound screening for AAA is recommended for all women at or older than 65 years with a family history of AAA or who have smoked
- Re-screening patients for AAA is not recommended if an initial ultrasound scan performed on patients 65 years of age or older demonstrates an aortic diameter of <2.6 cm.
Vascular disease can block the carotid artery blood flow to the brain and cause strokes. Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States. Each year, 140,000 people die annually from this disorder. A large proportion of strokes is caused by plaque in the carotid arteries. In 2020, Americans paid about US $67 billion for stroke-related medical costs and disability and the cost is expected to climb to over $400 billion by 2050. (American Heart Association).
Vascular disease can impair circulation to the legs, leading to a reduced ability to walk and in some cases, leg amputation. Vascular disease in the legs is a major indicator for heart disease. One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has peripheral arterial disease (PAD). It affects 19-21 million people in the United States as of 2020 (evtoday.com). Individuals with PAD suffer a five-fold increased relative risk of a cardiovascular ischemic event and total mortality that is two-three fold greater than those without PAD. Therefore, screening for PAD not only identifies patients with asymptomatic PAD in whom risk factor modification can slow or stop the progression of the disease process, but also allows identification of individuals who may also may be at risk of heart attack and stroke due to blockages affecting these organ systems.
CT Coronary Angiography
This highly detailed examination is performed by injecting a contrast material into a vein in the patient’s arm, which then will enhance seeing the coronary vessels. This will make it possible to obtain a complete 3-D scan of the heart. The actual scan takes only 20 seconds, within an examination time of 30 minutes. The precise results of this examination will give the patient’s doctor information about the condition of the patient’s coronary vessels.
Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) – in the event there is an obstruction in one or more of the coronary vessels, Pueblo Radiology can conduct an FFR analysis. This is an Al analysis that evaluates the heart’s blood flow relative to the obstruction. Significant obstructions in flow might be cause for more aggressive treatment (e.g. stents), where sufficient flow past an obstruction may dictate a more conservative treatment plan.
FAQs
You belong to a high-risk group if any of the following factors apply to you:
- You have high cholesterol levels
- You have high triglyceride values
- You smoke
- You have high blood pressure
- You are hereditarily at risk
- You have diabetes
Or any of the factors in combination with a sedentary lifestyle. If one or more of the above points apply to you, contact your physician to find out more about how CT can help in the evaluation of your heart.
Usually your appointment will be 60 minutes. The first 30 minutes will have you lying down as we monitor your blood pressure and pulse. We will also give you a drug that slows your heart rate. A slower heart rate provides a much better study. Your “table time” on the scanner will be about 30 minutes while the actual scan is only 15-20 seconds.
Interventional Procedures
What ARE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES?
Pueblo Radiology has several physicians that are experienced and/or fellowship trained in interventional procedures. These procedures involve minimally invasive techniques with the guidance of X-ray, CT and/or Ultrasound. We provide consultations, treatment and follow-up in our outpatient office. While a majority of the procedures we perform can be easily and safely done at our outpatient office, there are a few procedures that require the use of a hospital “cath-lab” or surgery suite. Most of these hospital based procedures are performed as outpatients and patients are discharged the same day; occasionally there will be a need for further hospitalization and observation.
The location of your procedure (hospital vs. office) will ultimately be determined by your medical condition, the complexity of the procedure, your medical history and the information discussed between your doctor and our radiologist.
PROCERDURE VIDEOS
Epidural Spine Injection
An epidural steroid injection (ESI) is the delivery of powerful anti-inflammatory medicine directly into the space outside of the sac of fluid around your spinal cord. This area is called the epidural space. Dr. Lawrence Harter, explains what to expect from your exam.
Joint Injection
A steroid injection is a minimally invasive procedure that can temporarily relieve pain caused by an inflamed joint. The cause of joint pain (arthritis, injury, degeneration) is not well understood. The procedure has two purposes. First, it can be used as a diagnostic test to see if the pain is actually coming from the joint. Second, it can be used as a treatment to relieve inflammation and pain caused by various conditions.
;
Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy
An ultrasound-guided breast biopsy uses sound waves to help locate a lump or abnormality and remove a tissue sample for examination under a microscope.
PUEBLO RADIOLOGY’S INTERVENTIONAL SPECIALISTS
Pain Management
What is pain managment?
Sometimes in the pursuit of better health we overdo things or, in other cases, our bodies are just not used to our new exercise routine. In these situations, slowing down, rest, and consultation with your physician are recommended. In some instances, when the pain is not responsive to more conservative treatments, pain management procedures can be performed. These procedures can reduce the patient’s current pain and provide a path for longer term pain relief through calming the associated inflammation so as to promote healing.
Pueblo Radiology has long provided pain management services in our Bath Street office. Commonly, the injected medications consist of a short-term anesthetic for pain relief (Lidocaine) in combination with a long-acting corticosteroid (dexamethasone) to promote healing. Our studies are imaging guided, meaning that our physicians monitor the process through use of real-time imaging. Studies have shown that image-guided treatments are far more effective for the patient as the medication is injected accurately, in the problem area.
At Our Office, The Following Procedures Are Performed:
The procedures below require an order from your physician.
Epidural Spine Injection
An epidural injection is a procedure where our radiologist injects anesthetic and corticosteroid medications into the area around the spinal cord called the epidural space. Epidural injections provide pain relief from various spinal conditions such as spinal stenosis, sciatica, and degenerative disc disease.
TransforamInal Injection (Spine)
Transforaminal injections are made directly into the area of the neural foramen, where the nerves exit the spinal canal and adjacent to the articular facets. The injection is image-guided, and is designed to reduce pain and inflammation around the existing nerve.
Facet Joint Injection (Spine)
A facet injection is the injection of anesthetic and/or corticosteroid medications into the facet joint(s) of the spine. This procedure is image-guided and is done to alleviate back pain.
Joint Injections
Joint injections involve the injection of anesthetic and/or corticosteroid medications directly into the joint space. The procedure is image-guided and performed by our radiologists.
Tendon Injections
Tendon injections are performed by our radiologists using some form of imaging guidance, typically ultrasound. A corticosteroid and/or anesthetic medication will be injected precisely in the area of pain and inflammation.
Bursa Injections (Around Major
Joints)
Bursa injections are performed by our radiologist using some form of image guidance, typically ultrasound. A corticosteroid and anesthetic medication will be injected precisely into the painful and inflamed bursa.





